General How to characterise FETs quickly
2013/10/18As fundamental components of many devices and electronic instruments, field effect transistors (FETs) are important semiconductor devices.
A FET is a majority charge-carrier device in which the current-carrying capability is varied by an applied electric field. It has three main terminals: the gate, the drain, and the source. A voltage applied to the gate terminal (VG) controls the current that flows from the source (IS) to the drain (ID) terminals.
There are many types of FETs, including the mosfet (metal-oxide-semiconductor), mesfet (metal-semiconductor), JFET (junction), organic FET, graphene nano-ribbon (GNRFET) and carbon nanotube (CNTFET). These FETs differ in the design of their channels. FETs are used in a variety of applications including as amplifiers, memory devices, switches, logic devices, and sensors.
Characterising their current-voltage (I-V) parameters is crucial to ensuring they meet specifications and work properly in their intended applications. These I-V tests may include gate leakage, breakdown voltage, threshold voltage, transfer characteristics, drain current and on-resistance. FET testing often involves programming and synchronising several instruments, including multiple sensitive ammeters and voltage sources, which can be tedious and time consuming.
Although a turnkey semiconductor characterisation system solves the integration problem, systems of this type typically cost tens of thousands of dollars. A third approach involves using an instrument called a source measure unit (SMU) that can accurately source and measure both current and voltage.
The number of SMUs required in the test usually depends on the number of FET terminals that must be biased and/or measured.
This article outlines how to make faster I-V measurements on FETs using SMU instruments, a growing number of which include software tools that simplify device characterisation. For example, Keithley’s series 2600B family of one- and two-channel SMUs have current resolution to 0.1fA and can be current limited to prevent damage to the device.
Using an SMU for FET testing
A FET’s I-V characteristics can be used to extract many device parameters, to study the effects of fabrication techniques and process variations, and to determine the quality of the contacts.
Figure 1 illustrates a DC I-V test configuration for a mosfet using a two-channel SMU (CH1 and CH2). Here, the Force HI terminal of SMU CH1 is connected to the gate of the MOSFET and the Force HI terminal of SMU CH2 is connected to the drain.
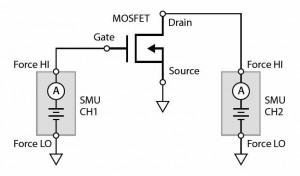
FET test circuit
The source terminal of the mosfet is connected to the Force LO terminals of both SMU channels or to a third SMU channel if it is necessary to source and measure from all three terminals of the mosfet.
Once the device is set up and connected to the SMU, the control software, often an embedded software tool, must be configured to automate the measurements.
After connecting the instrument to any computer with an Ethernet cable, entering the IP address of the SMU into the URL line of any web browser will open the instrument’s web page. From that page, the user can launch the embedded software and configure the desired test or tests, which can often be saved and recalled for future use.
One I-V test commonly performed on a mosfet is the drain family of curves (VDS-ID). With this test, SMU CH1 steps the gate voltage (VG) while SMU CH2 sweeps the drain voltage (VD) and measures the resulting drain current (ID).
Once the two SMU channels are configured to perform the test, the data can be generated and plotted on the screen in real time. Once exported to a .csv file, this I-V data can be imported into a spreadsheet for further analysis or displayed in table view.
Another common I-V FET test this same configuration supports is Drain current (ID) as a function of gate voltage (VG). For this test, the gate voltage is swept and the resulting drain current is measured at a constant drain voltage.
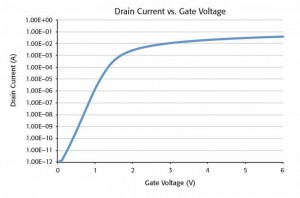
Drain current plot
Figure 2 shows the results of an ID-VG curve at a constant drain voltage. However, in this case, the generated data was exported to a file and plotted on a semi-log graph. This test can be easily reconfigured to step the drain voltage as the gate voltage is swept. The ID-VG data shows the many decades of drain current that the SMU measured, from 1E-12 to 1E-2A
This test can be easily reconfigured to step the drain voltage as the gate voltage is swept. The ID-VG data shows the many decades of drain current that the SMU measured, from 1E-12 to 1E-2 amps. When measuring low current, it’s crucial to employ low level measurement techniques, such as shielding and guarding, to prevent errors.
Shielding usually implies the use of a metallic enclosure to prevent electrostatic interference from affecting a high impedance circuit.
Guarding implies the use of an added low impedance conductor, maintained at the same potential as the high impedance circuit, which reduces the leakage current in the test circuit. A guard doesn’t necessarily provide shielding.
Mary Anne Tupta, senior staff applications engineer, Keithley Instruments
Welcome to SUV System Ltd!
SUV System Ltd is ISO 90012008 Certified electronics distributor with 10 years of experiences.
We have built up long term business relationship with about many companies which are stockers and authorized agents. we have a steady and reliable supply to meet customer's demands to the greatest extent .Confidently, we are able to lower your cost and support your business with our years of professional service.
SUV System Ltd is Electronic Components Distributor Supplies,Find Quality Electronic Components Supplies Products IC(Integrated Circuits),Connectors,Capacitor,Resistors,Diodes,Transistors,LED at Suvsystem.com. Sourcing Other Energy, Environment, Excess Inventory Products from Manufacturers and Suppliers at Suvsystem.com
Electronic Components distributor:http://www.suvsystem.com
Connectors Distributor:http://www.suvsystem.com/l/Connectors-1.html
IC Distributor:http://www.suvsystem.com/l/IC(Integrated-Circuits)-1.html
LED Distributor:http://www.suvsystem.com/l/LED-1.html
Capacitor Distributor:http://www.suvsystem.com/l/Capacitor-1.html
Transistor Distributor:http://www.suvsystem.com/l/Transistors-1.html
Resistor Distributor:http://www.suvsystem.com/l/Resistors-1.html
Diode Distributor:http://www.suvsystem.com/l/Diodes-1.html
SUV System Ltd insists on the managing faith ofsincereness,speciality,foresight, win-win,so we build up stable-relationship customers located all over the world, including the States, Europe, Argentina, UAE, Malaysia, Australia,and India etc
we are focus on the following fields,and hope we can help you.
Diodes Inc Voltage Regulators Transistors TI IC FAIRCHILD diodes NXP Transistors BB IC Current Sensors Resistors ROHM Resistors LITTELFUSE Diodes NEC Transistors TOSHIBA Transistors AD IC Transistors VISHAY IC Connectors IR transistor Dialight LED Renesas parts IC Metal Can Packages Transistors ST Diodes Resistors IR Diodes SANYO IC Resistor Networks Kingbrigt LED Industrial IC Resistor Arrays Schottky Diodes MAXIM IC NS IC INFLNEON Diodes Fairchild Semiconductor Transistors Fast Recovery Diodes TOSHIBA Diodes MURATA IC Xilinx IC ON Diodes Chip Fuses Discrete Semiconductor Transistors Texas Instruments(TI) IC
http://www.suvsystem.com/a/6704.aspx